Ebola, a severe and often deadly viral illness, has been a major public health concern in recent years. The disease, which is caused by the Ebola virus, has had a significant impact on communities in West and Central Africa, resulting in widespread illness and death. In this article, we will delve into the causes, symptoms, treatment, and transmission of Ebola, providing a comprehensive overview of this complex and often misunderstood disease.
Cause of Ebola
Ebola is caused by the Ebola virus, which is a member of the Filoviridae family of viruses. The virus is typically found in animals, such as fruit bats and nonhuman primates, and can be transmitted to humans through direct contact with infected animals or their bodily fluids. The virus can also be spread through human-to-human contact, often through touching or caring for an infected person.
Symptoms of Ebola
The symptoms of Ebola can vary, but typically begin with fever, headache, and muscle pain. As the disease progresses, symptoms can include vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and bleeding or bruising. In severe cases, Ebola can cause seizures, coma, and even death. The incubation period of Ebola, which is the time between exposure to the virus and the onset of symptoms, can range from 2 to 21 days.
Treatment of Ebola
While there is no cure for Ebola, treatment typically involves supportive care, such as providing fluids, oxygen, and medication to manage symptoms. In some cases, experimental treatments, such as ZMapp and Remdesivir, may be used to help manage the disease. It is essential to seek medical attention immediately if symptoms of Ebola are present, as early treatment can improve outcomes.
Transmission of Ebola
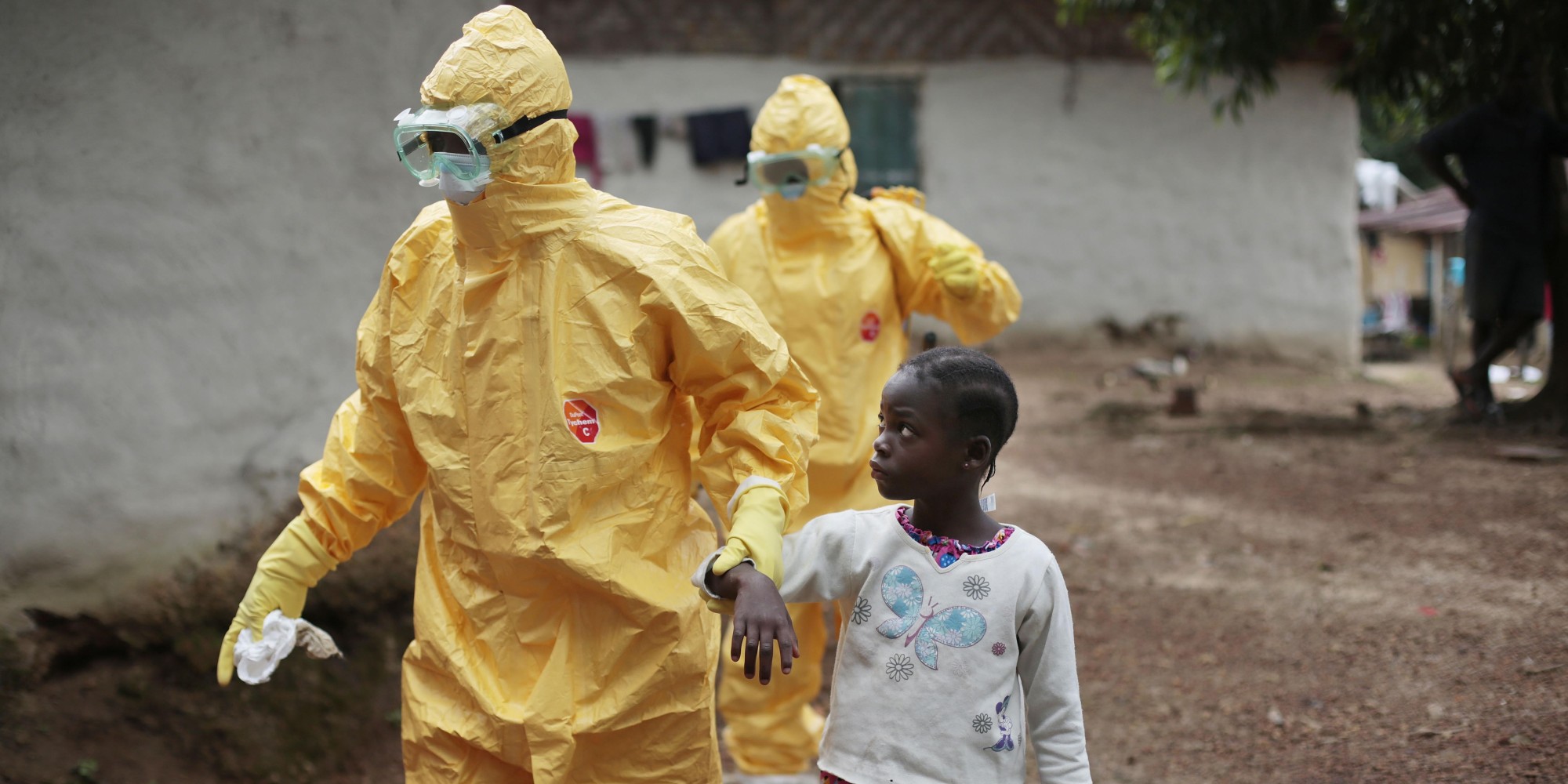
Ebola is primarily spread through human-to-human contact, often through touching or caring for an infected person. The virus can also be spread through contact with contaminated bodily fluids, such as blood, sweat, and saliva. In addition, Ebola can be spread through contact with contaminated objects, such as needles and medical equipment. To prevent the spread of Ebola, it is essential to practice good hygiene, such as washing hands frequently and avoiding close contact with people who are sick.
Prevention and Control
Preventing and controlling the spread of Ebola requires a multifaceted approach. This includes:
Practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands frequently
Avoiding close contact with people who are sick
Wearing personal protective equipment (PPE) when caring for an infected person
Using proper infection control procedures when handling contaminated objects or bodily fluids
Implementing public health measures, such as contact tracing and quarantine
By understanding the causes, symptoms, treatment, and transmission of Ebola, we can work towards preventing and controlling the spread of this deadly disease. It is essential to stay informed and take steps to protect ourselves and our communities from the risks associated with Ebola.
Ebola is a complex and often misunderstood disease that requires a comprehensive approach to prevention and control. By understanding the causes, symptoms, treatment, and transmission of Ebola, we can work towards reducing the risk of infection and improving outcomes for those affected. If you have any concerns about Ebola or would like to learn more, please consult a healthcare professional or visit a reputable online resource, such as the
Britannica website.

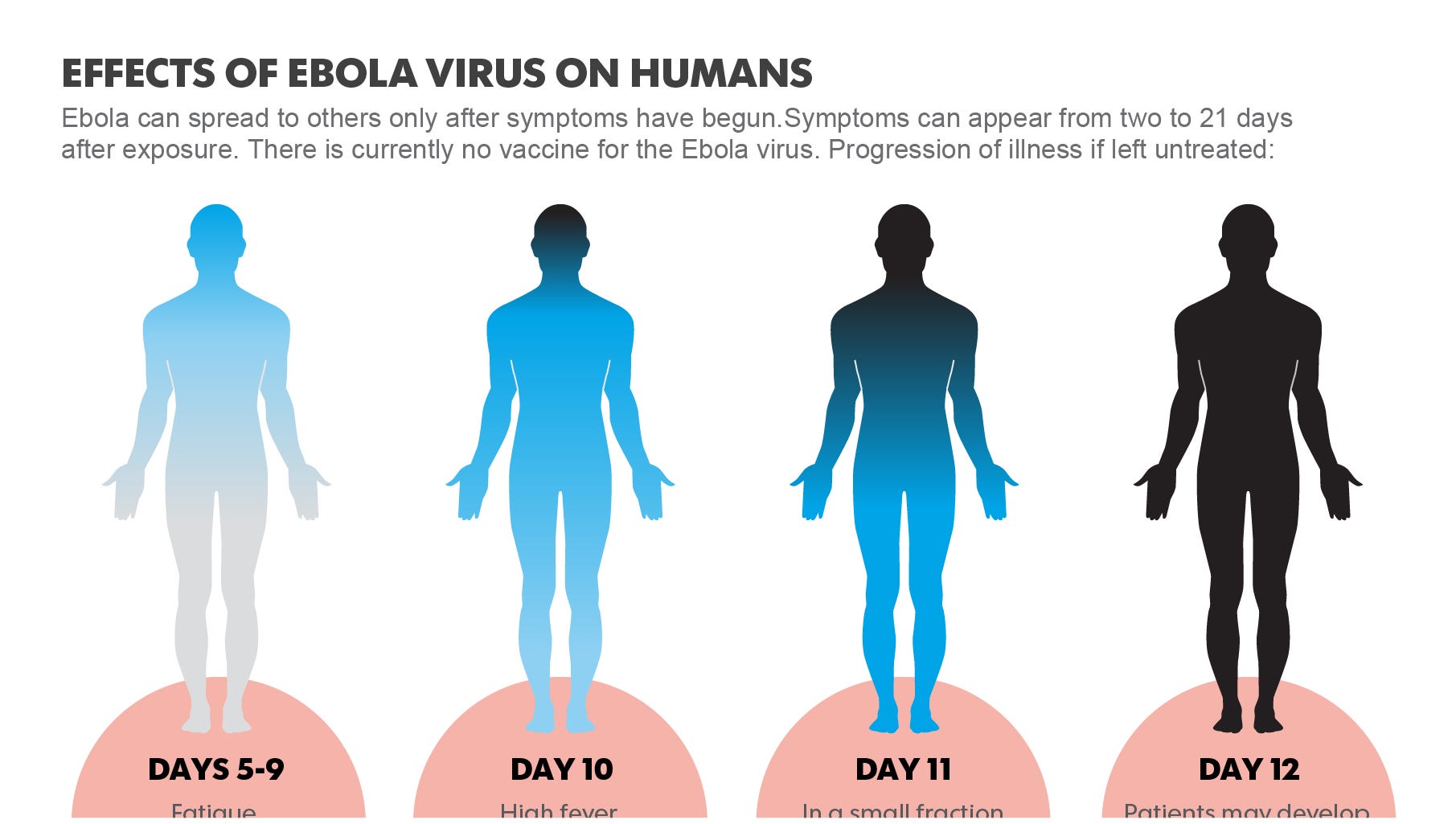
/EbolaVirus-5b7c3f08c9e77c0057d4924d.jpg)